The Ultimate Glossary of Marketplace Terms You Should Know
Get to know all the marketplace-related terms and their definition with our marketplace glossary of terms.
In this article, you will get to know all the marketplace-related terminologies, their definition, and also some helpful resources in case you want to learn about them in-depth.
Marketplace glossary of terms
- Online marketplace
- Churn rate
- Supply and demand
- Service provider
- B2B marketplace
- B2C marketplace
- Two-sided marketplace
- P2P marketplace
- Inventory
- Business niche
- Handyman
- Service marketplace
- Cart abandonment
- Retention rate
- Conversion rate
- Cross-selling
- Customer lifetime value
- Customer acquisition cost
- Rental marketplace
- Payment gateway
- Stripe
- Geo-fencing
- Fulfillment center
- Listing fee
- Service fee
- Delivery fee
- Referral program
- Recurring revenue
- Hyperlocal delivery
- Warehousing
- Upselling
- Ghost kitchens
- Push notification
- Business model
- Revenue model
- Hourly pricing
- Business structure
- Ratings and reviews
- Average Order Value (AOV)
- Purchase order
- Vendor
- ROI
- PCI Compliant
- Company incorporation
- Subscription model
- Meal-kit
- Brick and Mortar
- Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
- Logistics
- LLC
- Sole proprietorship
- Partnership
- Checkout page
- Minimum Order Value (MOV)
- Out of stock
- In stock
- Supply chain
- Unique Selling Proposition
- Billing address
- Delivery address
- Shipping cost
- Invoice
1. Online marketplace
What is an online marketplace?
An online marketplace is a web or app-based platform that acts as a bridge to connect buyers and sellers. And they have product/service inventories from various sellers.
Examples of online marketplaces:
-
Amazon
-
eBay
-
Alibaba
-
Airbnb
-
Uber
-
Etsy
-
Upwork
-
Rover
-
YourMechanic
-
ZocDoc
Types of online marketplaces:
-
B2B
-
B2C
-
P2P
-
Vertical marketplaces
-
Horizontal marketplaces
-
On-demand marketplaces
How do online marketplaces earn money?
Here are the revenue models that an online marketplace can use:
-
Commission-based
-
Subscription-based
-
Listing fee model
-
Featured listing or ads within the platform
👉 Learn how to build an online marketplace here
2. Churn rate
What is the churn rate?
A churn rate, customer churn, or attrition rate is the rate of time when a customer decides to quit doing business with a company.
How to calculate the churn rate?
You have to divide the total number of customers lost in a specific time frame by the number of customers gained at the start of the time frame and multiply it by 100.
Churn rate formula: (Total number of customers lost/total number of customers at the start of the time frame) * 100.
What is a good churn rate?
A good churn rate should be in the range of 5 - 9%. It might vary depending on the industry you serve.
How to reduce the customer churn rate?
-
Provide the best customer support.
-
Concentrate on quality over anything.
-
Understand your customer needs and segment them.
-
Personalize your message based on the segment.
-
Think of ways to be in constant touch with your customers.
-
Gather feedback and improve further.
-
Send automated abandonment cart emails & push notifications.
-
Enhance UX and simplify the onboarding process.
3. Supply and demand
Definition of Supply and Demand:
Supply and demand is an economic model that describes the affinity between the product pricing and the demand or supply of the same.
When a product price increases, the supply will also increase, and the demand among the customers will decrease and vice versa.
Supply:
Supply in economics refers to a quantity of a product that a manufacturer is willing and able to produce.
Demand:
Demand in economics refers to the number of customers willing and able to purchase goods/services.
👉 Learn how to solve supply and demand problem in marketplace here
4. Service provider
Definition:
A service provider is a person or a company that provides services to other people or companies.
5. B2B marketplace
A B2B marketplace is an online platform where one business sells its service to other businesses and vice versa.
Examples of B2B marketplaces:
-
Upwork
-
Alibaba
-
Designrush
6. B2C marketplace
A B2C marketplace is an online platform where a business sells its products directly to the end customers.
Examples of B2C marketplaces:
-
Amazon
-
Etsy
-
Poshmark
-
eBay
-
Walmart
7. Two-sided marketplace
A two-sided marketplace is a platform where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods and services.
A two-sided marketplace should benefit both buyers and sellers.
Examples of two-sided marketplaces:
-
Uber
-
Airbnb
-
Netflix
-
Upwork
-
Fiverr
👉 Learn more about two-sided marketplace here
8. P2P marketplace
Peer to Peer [P2P] marketplace is an online platform that connects people who need a service or product with the people who rent or sell them.
Examples of P2P marketplaces:
-
Airbnb
-
Uber
-
Taskrabbit
-
Kickstarter
-
eBay
Industries that P2P marketplaces can serve:
-
Fintech
-
Rentals
-
Transport
-
Edtech
-
eCommerce
👉 Learn more about peer to peer marketplace here
9. Inventory
Definition:
Inventory is goods, raw materials, or assets that are held by a business either for production or to sell to make a profit.
10. Business niche
Definition:
Niche is a specialized area of expertise within a wider market in which a business operates to set itself apart from its competitors and provide better service to its customers.
How to choose a business niche?
-
Explore what you love to do.
-
Find a problem that people like you face.
-
Find a solution to that problem.
-
Analyze the market
-
Test your offer
👉 Learn how you can pick your online business niche here
11. Handyman
A handyman is a person who is skilled at repairing things, especially in and around the house.
Types of handyman services
-
Painting
-
AC or other electricals installation
-
Plumbing
-
Drywall repair
-
Tile laying
-
Furniture assembly
-
Cleaning services
-
Yard works
👉 Learn how you can build a handyman app here
12. Service marketplace
A service marketplace is an online platform where individual professionals and businesses can sell or get services.
Examples of service marketplaces
- Upwork
- TaskRabbit
- Thumbtack
- Fiverr
- Handy
👉 Learn how you can build a service marketplace app here
13. Cart abandonment
Cart abandonment is when a customer adds a product or service to the cart and leaves without purchasing them.
👉 Learn about sending abandoned cart email campaigns here
14. Retention rate
Retention rate is a percentage of customers a marketplace retains over a specific period of time.
15. Conversion rate
Conversion rate is a percentage of marketplace website visitors that convert into paying customers by completing the desired conversion action.
Conversion actions will differ from one site to another. Some conversion actions are,
- Sign up
- Make a purchase
- Download an e-book
- Submitting a lead form
16. Cross-selling
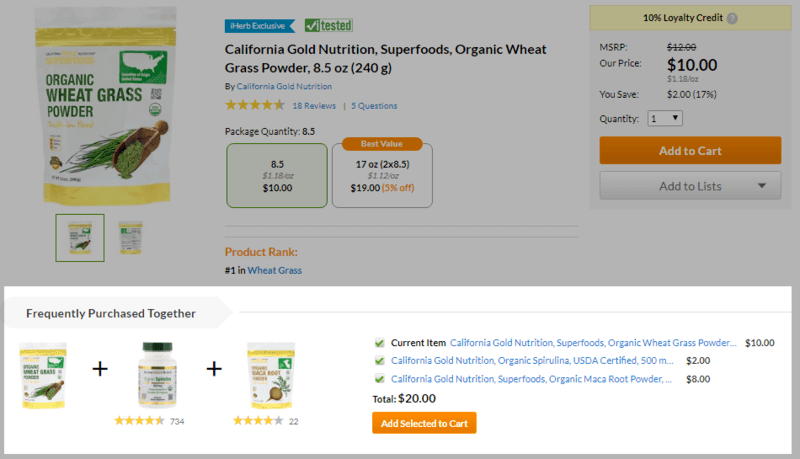
Cross-selling is the process of recommending products or services to customers that are related to the one being purchased.
Here is an example of cross-selling:
17. Customer lifetime value
Customer lifetime value is a metric that measures the revenue a business can make from a single customer over their entire lifetime with the business.
18. Customer acquisition cost
Customer acquisition cost is the cost associated with acquiring a new paying customer.
A CAC:LTV ratio of 1:3 is considered better when measuring customer acquisition cost.
19. Rental marketplace
A rental marketplace is an online platform where individuals or businesses rent out their goods for a specific period of time.
Examples of rental marketplace platforms are Airbnb, Turo, Uber, etc.
👉 Here's a step by step guide to start an online rental business
20. Payment gateway
Payment gateways is an online service that helps sellers or merchants to accept payments from customers across multiple payment modes such as cards, UPIs, etc.
21. Stripe
Stripe is one of the many payment gateways that process credit and debit card payments to enable sellers or merchants to accept payment online.
22. Geo-fencing
Geo-fencing is a virtual boundary on the real-world geographical area used by location-sensitive businesses to deliver services when the device enters that boundary.
23. Fulfillment center
A fulfillment center is used by businesses to pick, pack, and deliver goods that the customers ordered.
24. Listing fee
A listing fee is a small amount you have to pay the marketplaces to list your product or service on their platform.
25. Service fee
A service fee is a small amount that the customers pay for every order they place on the marketplace platform.
26. Delivery fee
A delivery fee is a nominal fee that the customers pay for the delivery of their product ordered on the marketplace platform.
27. Referral program
The referral program is a process used by marketplaces to incentivize customers when they refer the products to their friends and family.
28. Recurring revenue
The recurring revenue model is a predictive and stable revenue that a business generates at regular intervals and expects to continue in the future.
29. Hyperlocal delivery
Hyperlocal delivery is the process of collecting goods from the local sellers and delivering them straight to the customers' doorsteps.
👉 Learn more about hyperlocal delivery here
30. Warehousing
Warehousing is the process of storing the goods in a storage facility for distribution. Warehouses are places where the goods are stored safely.
31. Upselling
Upselling is a sales approach that encourages customers to buy the premium or higher-end version of a product rather than the one they originally chose.
32. Ghost kitchens
Ghost kitchen is nothing but a restaurant operating without a dine-in facility and focuses mainly on serving orders from food delivery apps.
33. Push notification
Push notification is tiny messages or alerts that appear on the user's mobile or desktop to make them take action.
It can only be sent if the user has installed the application on their device.
34. Business model
A business model is a framework on which a company operates to deliver value to potential customers and make money.
Types of marketplace business model
- B2B - Business to Business
- B2C - Business to Customers
- P2P - Peer to Peer
👉 Learn more about the marketplace business models here
35. Revenue model
A revenue model is a part of a business plan which dictates how a company will generate its revenue.
Types of marketplace revenue model
- Commission based
- Subscription-based
- Listing-based.
- Freemium
36. Hourly pricing
Hourly pricing is when a company or an individual charges a certain amount per hour for their service.
37. Business structure
A business structure is a legal representation of how a business is formed, and it helps achieve organizational objectives.
Types of business structure
-
Sole proprietorship
-
Partnership
-
LLC - Limited Liability Company
-
Corporation
38. Ratings and reviews
Ratings & reviews help customers to share feedback about your product or service in terms of star ratings and text comments.
39. Average Order Value (AOV)
Average Order Value (AOV) is the average amount spent by customers on each order they place on your platform.
How to calculate the Average Order Value?
The average order value is calculated by dividing total revenue by the number of orders placed over a specific time period.
AOV = Total revenue / Number of orders.
40. Purchase order
A purchase order is a document sent by buyers to sellers to place an order with them. It includes details such as the list of products needed, their quantity, expected delivery date, etc.
41. Vendor
A vendor or seller is an individual or business that sells products or services to others in exchange for money.
For example, Amazon doesn't make its products and sells them to customers. Vendors are invited to post their products on their marketplace and are paid when a customer purchases a product.
42. ROI
Return of Investment (ROI) is a financial metric used to measure the profitability of an investment you made.
43. PCI Compliant
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a payment security standard to be followed by companies that accept, process, and store the private payment data of a cardholder.
44. Company incorporation
Incorporation is a legal procedure for a business to become a corporation.
45. Subscription business model
The subscription business model is used by companies that offer their products or services for a monthly recurring fee.
46. Meal-kit
A meal kit is a subscription-based food delivery model where a company delivers pre-determined ingredients and easy-to-follow cooking tips to prepare food in the comfort of your home.
47. Brick and Mortar
Brick and mortar refer to a traditional store having one or more physical location offering products or service directly to customers.
48. Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
Key performance indicators (KPI) are the quantifiable metrics used to measure the critical business performance over a period of time.
49. Logistics
Logistics is a business operation of planning the flow of goods from the source to the point of consumption.
50. LLC
A limited liability company [LLC] is a legal business structure or entity for a private business in the U.S which protects its owner from personal liabilities.
51. Sole proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is an unincorporated business owned and operated by a single owner. It is the easiest business structure that one starts almost immediately.
52. Partnership
A partnership is a business structure where a business' liability and profits are shared equally between two or more partners.
53. Checkout page
Checkout pages are the pages that appear on marketplace stores during the payment process.
54. Minimum Order Value (MOV)
The minimum order value is the minimum amount that a customer should spend to get their ordered product to be shipped.
55. Out of stock
Out of stock is when a product in a marketplace store is unavailable for a customer to order.
56. In stock
In stock is when a product in a marketplace store is available for a customer to order.
57. Supply chain
The supply chain is a network of companies and suppliers to produce and distribute products to the end customers.
58. Unique Selling Proposition
A unique selling proposition is a single benefit that differentiates your product from the competition.
59. Billing address
A billing address is an address associated with a customer's payment methods, which can be credit or debit cards.
60. Delivery address
Delivery address is the customer's address where the ordered items to be delivered.
61. Shipping cost
Shipping costs are the expenses incurred in transporting a product from its origin to the end customer.
62. Invoice
An invoice or bill is a document provided by the seller to the customer at the end of a purchase or transaction.





